FANCE

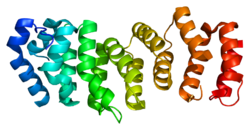
2ILR217872775ENSG00000112039ENSMUSG00000007570Q9HB96n/aNM_021922NM_001163819NM_001163820NM_028348NP_068741n/aFanconi anemia, complementation group E protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FANCE gene. The Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, and FANCL. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA cross-linking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation groufcrp E.2ilr: Crystal structure of human Fanconi Anemia protein E C-terminal domain Fanconi anemia, complementation group E protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FANCE gene. The Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, and FANCL. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA cross-linking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation groufcrp E. A nuclear complex containing FANCE protein (as well as FANCC, FANCF and FANCG) is essential for the activation of the FANCD2 protein to the mono-ubiquitinated isoform. In normal, non-mutant cells, FANCD2 is mono-ubiquinated in response to DNA damage. FANCE together with FANCC acts as the substrate adapter for this reaction Activated FANCD2 protein co-localizes with BRCA1 (breast cancer susceptibility protein) at ionizing radiation-induced foci and in synaptonemal complexes of meiotic chromosomes. Activated FANCD2 protein may function prior to the initiation of meiotic recombination, perhaps to prepare chromosomes for synapses, or to regulate subsequent recombination events. FANCE is stated to have been expressed in 151 organs with the highest level in female gonads. The location of the gene is in 6p21.31, where p is the short arm of chromosome 6 at position 21.31 The location at molecular level is in base pairs 35,452,339 to 35,467,106 on chromosome 6 (Homo sapiens Annotation Release 109, GRCh38.p12) The main complex of FA contains a nuclear multi-subunit complex of notably 8 FA proteins. This adds a single ubiquiting chain to the FANCD2 following DNA damage or duplicative pressure. For the collection of FANCC, FANCE is important in the nucleus and gathering of the core complex. Some characteristics of FANCE is that it can set itself with ubiquitinated FANCD2, BRCA2 and constructed nuclear foci. Also, as it is the only member showing direct union with FANCD2 and gives the needed links between FA core complex and FANCD2. The structure of FANCE has an epitope on its surface that is found to be important for its binding with FANCD2. The existence of recurrent helical motif was not clear when analysis of amino acids were done. It consists of 13 α-helices, 1 310-helix and no β-strand. Long shaped, non-globular shape and 70 Å n size. Width of 30 Å and thickness 20 Å. The protein folds continuously in right-handed manner from N- to C- terminal. Identifying it is easy because of its helices at the end of C-end.