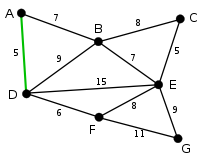
Kruskal's algorithm

Kruskal's algorithm is a minimum-spanning-tree algorithm which finds an edge of the least possible weight that connects any two trees in the forest. It is a greedy algorithm in graph theory as it finds a minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph adding increasing cost arcs at each step. This means it finds a subset of the edges that forms a tree that includes every vertex, where the total weight of all the edges in the tree is minimized. If the graph is not connected, then it finds a minimum spanning forest (a minimum spanning tree for each connected component). Kruskal's algorithm is a minimum-spanning-tree algorithm which finds an edge of the least possible weight that connects any two trees in the forest. It is a greedy algorithm in graph theory as it finds a minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph adding increasing cost arcs at each step. This means it finds a subset of the edges that forms a tree that includes every vertex, where the total weight of all the edges in the tree is minimized. If the graph is not connected, then it finds a minimum spanning forest (a minimum spanning tree for each connected component). This algorithm first appeared in Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, pp. 48–50 in 1956, and was written by Joseph Kruskal. Other algorithms for this problem include Prim's algorithm, Reverse-delete algorithm, and Borůvka's algorithm.