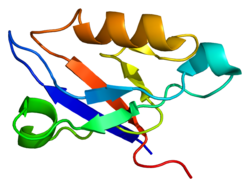
LDB3

4YDP1115524131ENSG00000122367ENSMUSG00000021798O75112Q9JKS4NM_007078NM_001368063NM_001368064NM_001368065NM_001368066NM_001368067NM_001368068NM_001039076NM_011918NP_009009NP_001354992NP_001354993NP_001354994NP_001354995NP_001354996NP_001354997NP_001034165NP_036048LIM domain binding 3 (LDB3), also known as Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif (ZASP), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LDB3 gene. ZASP belongs to the Enigma subfamily of proteins and stabilizes the sarcomere (the basic units of muscles) during contraction, through interactions with actin in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Mutations in the ZASP gene has been associated with several muscular diseases.1rgw: Solution Structure of ZASP's PDZ domain1wjl: Solution structure of PDZ domain of mouse Cypher protein LIM domain binding 3 (LDB3), also known as Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif (ZASP), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LDB3 gene. ZASP belongs to the Enigma subfamily of proteins and stabilizes the sarcomere (the basic units of muscles) during contraction, through interactions with actin in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Mutations in the ZASP gene has been associated with several muscular diseases. ZASP is a PDZ domain-containing protein. PDZ motifs are modular protein-protein interaction domains consisting of 80-120 amino acid residues. PDZ domain-containing proteins interact with each other in cytoskeletal assembly or with other proteins involved in targeting and clustering of membrane proteins. ZASP interacts with alpha-actinin-2 through its N-terminal PDZ domain and with protein kinase C via its C-terminal LIM domains. The LIM domain is a cysteine-rich motif defined by 50-60 amino acids containing two zinc-binding modules. This protein also interacts with all three members of the myozenin family. Human ZASP can exist in cardiac and skeletal cells as six distinct isoforms, based on alternative splicing of 16 exons. There are 2 ZASP short forms (Uniprot ID: O75112-6, 31.0 kDa, 283 amino acids; and Uniprot ID: O75112-5, 35.6 kDa, 330 amino acids); and 4 ZASP long forms (Uniprot ID: O75112-4, 42.8 kDa, 398 amino acids; Uniprot ID: O75112-3, 50.6 kDa, 470 amino acids; Uniprot ID: O75112-2, 66.6 kDa, 617 amino acids; and Uniprot ID: O75112, 77.1 kDa, 727 amino acids). All ZASP isoforms have an N-terminal PDZ domain; internal, conserved sequences known as ZASP-like motifs (ZMs); and the four long isoforms have three C-terminal LIM domains. ZASP functions to maintain structural integrity of sarcomeres during contraction, and has been shown to be involved in protein kinase A signaling. ZASP has also been shown to co-activate α5β1 integrins along with the protein TLN1. Mutations in ZASP have been associated with myofibrillar myopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, noncompaction cardiomyopathy, and muscular dystrophy. The PDZ domain of ZASP binds the C-terminus of alpha actinin-2 and ZMs bind the rod domain of alpha actinin-2. The LIM domains have been shown to interact with protein kinase C. The cardiac-specific region of ZASP encoded by exon 4 includes a ZP motif and binds a regulatory subunit of protein kinase A. This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.