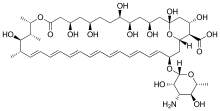
Amphotericin B

Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given with flucytosine. It is typically given by injection into a vein.MIC breakpoint (mg/L)Chagas disease: nitroimidazole (Benznidazole#)Pentavalent antimonials (Meglumine antimoniate#, Sodium stibogluconate) Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given with flucytosine. It is typically given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include a reaction with fever, chills, and headaches soon after the medication is given, as well as kidney problems. Allergic symptoms including anaphylaxis may occur. Other serious side effects include low blood potassium and inflammation of the heart. It appears to be relatively safe in pregnancy. There is a lipid formulation that has a lower risk of side effects. It is in the polyene class of medications and works in part by interfering with the cell membrane of the fungus. Amphotericin B was isolated from Streptomyces nodosus in 1955 and came into medical use in 1958. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. The cost in the developing world of a course of treatment as of 2010 is between 162 and US$229. One of the main uses of amphotericin B is treating a wide range of systemic fungal infections. Due to its extensive side effects, it is often reserved for severe infections in critically ill, or immunocompromised patients. It is considered first line therapy for invasive mucormycosis infections, cryptococcal meningitis, and certain aspergillus and candidal infections. It has been a highly effective drug for over fifty years in large part because it has a low incidence of drug resistance in the pathogens it treats. This is because amphotericin B resistance requires sacrifices on the part of the pathogen that make it susceptible to the host environment, and too weak to cause infection. Amphotericin B is often used in otherwise-untreatable protozoan infections such as visceral leishmaniasis and primary amoebic meningoencephalitis.