Deformational plagiocephaly

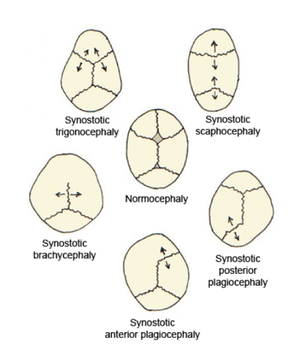
Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. It is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head caused by remaining in a supine position for prolonged periods. Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. It is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head caused by remaining in a supine position for prolonged periods. Plagiocephaly is the word that is used to describe a diagonal asymmetry across the head shape. This word particularly describes a flattening which is to one side at the back of the head and there is often some facial asymmetry. Plagiocephaly divides into two groups: synostotic plagiocephaly, with one or more fused cranial sutures, and nonsynostotic (deformational) plagiocephaly. Surgical treatment of these groups includes the deference method; however, the treatment of deformational plagiocephaly is controversial. Brachycephaly describes a very wide head shape with a flattening across the whole back of the head. Slight plagiocephaly is routinely diagnosed at birth and may be the result of a restrictive intrauterine environment giving a 'diamond' shaped head when seen from above. If there is premature union of skull bones, this is more properly called craniosynostosis. The incidence of plagiocephaly has increased dramatically since the advent of anti-Sudden Infant Death Syndrome recommendations for parents to keep their babies on their backs. Data also suggest that the rates of plagiocephaly is higher among twins and multiple births, premature babies, babies who were positioned in the breech position or back-to-back, as well as babies born after a prolonged labour. A developmental and physical assessment performed by a physician or a pediatric specialist is recommended. Often imaging is obtained if the diagnosis is questionable to see if the baby's sutures are present or not. If the sutures are not present, craniosynostosis may be ruled into question. Prevention methods include carrying the infant and giving the infant time to play on their stomach (tummy time), which may prevent the baby from progressing into moderate or severe plagiocephaly. The condition may improve to some extent as the baby grows, but in some cases, home treatment or physical therapy treatment can improve the shape of a baby’s head. Early interventions (based on the severity) are of importance to reduce the severity of the degree of the plagiocephaly.