Flesh-eating bacteria

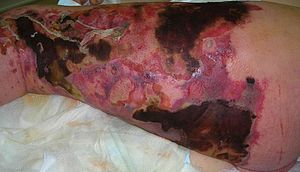
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), commonly known as flesh-eating disease, is an infection that results in the death of parts of the body's soft tissue. It is a severe disease of sudden onset that spreads rapidly. Symptoms include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. The most commonly affected areas are the limbs and perineum.The very first symptom of NF. The center is clearly getting darker red (purple).Early symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis. The darker red center is going black.The start of necrotizing fasciitisWound after aggressive acute debridement of NFNecrotic tissue from the left leg surgically removedPostsurgical debridement and skin graftingAfter knee disarticulation amputation Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), commonly known as flesh-eating disease, is an infection that results in the death of parts of the body's soft tissue. It is a severe disease of sudden onset that spreads rapidly. Symptoms include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. The most commonly affected areas are the limbs and perineum. Typically, the infection enters the body through a break in the skin such as a cut or burn. Risk factors include poor immune function such as from diabetes or cancer, obesity, alcoholism, intravenous drug use, and peripheral artery disease. It is not typically spread between people. The disease is classified into four types, depending on the infecting organism. Between 55 and 80% of cases involve more than one type of bacteria. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is involved in up to a third of cases. Medical imaging is helpful to confirm the diagnosis. Necrotizing fasciitis may be prevented with proper wound care and handwashing. It is usually treated with surgery to remove the infected tissue, and intravenous antibiotics. Often, a combination of antibiotics is used, such as penicillin G, clindamycin, vancomycin, and gentamicin. Delays in surgery are associated with a much higher risk of death. Even with high-quality treatment, the risk of death is between 25 and 35%. Necrotizing fasciitis occurs in about 0.4 people per 100,000 per year in the US, and about 1 per 100,000 in Western Europe. Both sexes are affected equally. It becomes more common among older people and is rare in children. It has been described at least since the time of Hippocrates. The term 'necrotizing fasciitis' first came into use in 1952. Symptoms may include fever, swelling, and complaint of excessive pain. The initial skin changes are similar to cellulitis or abscess, thus making the diagnosis at early stages difficult. Hardening of the skin and soft tissue and swelling beyond the area of skin changes are commonly present in those with early necrotizing changes. The redness and swelling usually blend into surrounding normal tissues. The overlying skin may appear shiny and tense. Other signs which are more suggestive of necrotizing changes (but present in later stages in 7 to 44% of the cases) are: formation of bullae, bleeding into the skin which is present before skin necrosis (skin turning from red to purple and black due to thrombosis of blood vessels), presence of gas in tissues, and reduced or absent sensation over the skin (due to the necrosis of the underlying nerves). Rapid progression to shock despite antibiotic therapy is another indication of necrotizing fasciitis. Necrotizing changes affecting the groin are known as Fournier gangrene. However, those who are immunocompromised (have cancer, use corticosteroid, on radiotherapy, chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, or prior organ or bone marrow transplantation) may not show normal symptoms. Immunocompromised persons also have twice the risk of death from necrotizing infections, so higher suspicion should be maintained in this group. More than 70% of cases are recorded in people with at least one of these clinical situations: immunosuppression, diabetes, alcoholism/drug abuse/smoking, malignancies, and chronic systemic diseases. For reasons that are unclear, it occasionally occurs in people with an apparently normal general condition. Necrotizing fasciitis can occur at any part of the body, but it is more commonly seen at the extremities, perineum, and genitals. Only a few of such cases arise from the chest and abdomen. Trauma is the usual cause of the infection, such as from intravenous drug injection, insulin injection, animal and insect bites, catheter insertion over the skin, or a fistula connecting skin to the internal body organs. Skin infections such as abscess and ulcers can also complicate necrotizing fasciitis. Spreading of infection through blood has been suggested for those with streptococcal pharyngitis. For infection of the perineum and genitals (Fournier gangrene), trauma, surgery, urinary tract infection, stones, and Bartholin gland abscess are the usual causes. The risk of developing necrotizing fasciitis from a wound can be reduced by good wound care and handwashing.