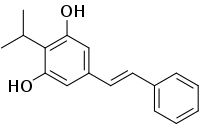
Benvitimod

Benvitimod (also known as tapinarof or 3,5-dihydroxy-4-isopropyl-trans-stilbene) is a bacterial stilbenoid produced in Photorhabdus bacterial symbionts of Heterorhabditis nematodes. It is a product of an alternative ketosynthase-directed stilbenoids biosynthesis pathway. It is derived from the condensation of two β-ketoacyl thioesters . It is produced by the Photorhabdus luminescens bacterial symbiont species of the entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis megidis. Experiments with infected larvae of Galleria mellonella, the wax moth, support the hypothesis that the compound has antibiotic properties that help minimize competition from other microorganisms and prevents the putrefaction of the nematode-infected insect cadaver. Benvitimod (also known as tapinarof or 3,5-dihydroxy-4-isopropyl-trans-stilbene) is a bacterial stilbenoid produced in Photorhabdus bacterial symbionts of Heterorhabditis nematodes. It is a product of an alternative ketosynthase-directed stilbenoids biosynthesis pathway. It is derived from the condensation of two β-ketoacyl thioesters . It is produced by the Photorhabdus luminescens bacterial symbiont species of the entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis megidis. Experiments with infected larvae of Galleria mellonella, the wax moth, support the hypothesis that the compound has antibiotic properties that help minimize competition from other microorganisms and prevents the putrefaction of the nematode-infected insect cadaver. Benvitimod is being studied in clinical trials for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.