Histone

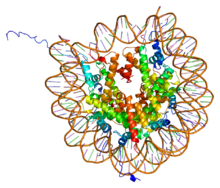
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and playing a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human diploid cell (containing 23 pairs of chromosomes) has about 1.8 meters of DNA; wound on the histones, the diploid cell has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin. When the diploid cells are duplicated and condensed during mitosis, the result is about 120 micrometers of chromosomes. In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and playing a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human diploid cell (containing 23 pairs of chromosomes) has about 1.8 meters of DNA; wound on the histones, the diploid cell has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin. When the diploid cells are duplicated and condensed during mitosis, the result is about 120 micrometers of chromosomes. Five major families of histones exist: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are known as the core histones, while histones H1/H5 are known as the linker histones. The core histones all exist as dimers, which are similar in that they all possess the histone fold domain: three alpha helices linked by two loops. It is this helical structure that allows for interaction between distinct dimers, particularly in a head-tail fashion (also called the handshake motif). The resulting four distinct dimers then come together to form one octameric nucleosome core, approximately 63 Angstroms in diameter (a solenoid (DNA)-like particle). Around 146 base pairs (bp) of DNA wrap around this core particle 1.65 times in a left-handed super-helical turn to give a particle of around 100 Angstroms across. The linker histone H1 binds the nucleosome at the entry and exit sites of the DNA, thus locking the DNA into place and allowing the formation of higher order structure. The most basic such formation is the 10 nm fiber or beads on a string conformation. This involves the wrapping of DNA around nucleosomes with approximately 50 base pairs of DNA separating each pair of nucleosomes (also referred to as linker DNA). Higher-order structures include the 30 nm fiber (forming an irregular zigzag) and 100 nm fiber, these being the structures found in normal cells. During mitosis and meiosis, the condensed chromosomes are assembled through interactions between nucleosomes and other regulatory proteins. Histones are subdivided into canonical replication-dependent histones that are expressed during the S-phase of cell cycle and replication-independent histone variants, expressed during the whole cell cycle. In animals, genes encoding canonical histones are typically clustered along the chromosome, lack introns and use a stem loop structure at the 3’ end instead of a polyA tail. Genes encoding histone variants are usually not clustered, have introns and their mRNAs are regulated with polyA tails. Complex multicellular organisms typically have a higher number of histone variants providing a variety of different functions. Recent data are accumulating about the roles of diverse histone variants highlighting the functional links between variants and the delicate regulation of organism development. Histone variants from different organisms, their classification and variant specific features can be found in 'HistoneDB 2.0 - Variants' database.