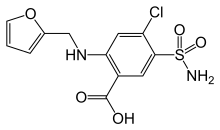
Furosemide

Furosemide, sold under the brand name Lasix among others, is a medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes. Furosemide, sold under the brand name Lasix among others, is a medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes. Common side effects include feeling lightheaded with standing, ringing in the ears, and sensitivity to light. Potentially serious side effects include electrolyte abnormalities, low blood pressure, and hearing loss. Blood tests are recommended regularly for those on treatment. Furosemide is a type of loop diuretic that works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Furosemide was patented in 1959 and approved for medical use in 1964. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, which lists the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale price in the developing world is between US$0.004 and US$0.02 per day. In the United States, it is available as a generic medication and costs about US$0.15 per day. In 2016, it was the 15th most prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 32 million prescriptions. It is on the World Anti-Doping Agency's banned drug list due to concerns that it may mask other drugs. It has also been used in race horses for the treatment and prevention of exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage. Furosemide is primarily used for the treatment of edema, but also in some cases of hypertension (where there is also kidney or heart impairment). It is often viewed as a first-line agent in most people with edema caused by congestive heart failure. Compared with furosemide, however, torsemide is associated with a lower risk of rehospitalization for heart failure and an improvement in New York Heart Association class of heart failure but no difference in the risk of death. Torsemide may also be safer than furosemide. Furosemide is also used for liver cirrhosis, kidney impairment, nephrotic syndrome, in adjunct therapy for swelling of the brain or lungs where rapid diuresis is required (IV injection), and in the management of severe hypercalcemia in combination with adequate rehydration. In chronic kidney diseases with hypoalbuminemia, it is used along with albumin to increase diuresis. It is also used along with albumin in nephrotic syndrome to reduce edema. Furosemide also can lead to gout caused by hyperuricemia. Hyperglycemia is also a common side effect. The tendency, as for all loop diuretics, to cause low serum potassium concentration (hypokalemia) has given rise to combination products, either with potassium or with the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride (Co-amilofruse). Other electrolyte abnormalities that can result from furosemide use include hyponatremia, hypochloremia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia. In the treatment of heart failure, many studies have shown that the long-term use of furosemide can cause varying degrees of thiamine deficiency, so thiamine supplementation is also suggested.