Cholesterol oxidase

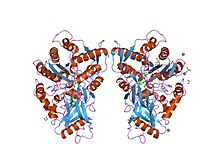
In enzymology, a cholesterol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction In enzymology, a cholesterol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are cholesterol and O2, whereas its two products are cholest-4-en-3-one and H2O2. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with oxygen as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol:oxygen oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include cholesterol- O2 oxidoreductase, 3beta-hydroxy steroid oxidoreductase, and 3beta-hydroxysteroid:oxygen oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in bile acid biosynthesis. The substrate-binding domain found in some bacterial cholesterol oxidases is composed of an eight-stranded mixed beta-pleated sheet and six alpha-helices. This domain is positioned over the isoalloxazine ring system of the FAD cofactor bound by the FAD-binding domain and forms the roof of the active site cavity, allowing for catalysis of oxidation and isomerisation of cholesterol to cholest-4-en-3-one. As of late 2007, 14 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1B4V, 1B8S, 1CBO, 1CC2, 1COY, 1I19, 1IJH, 1MXT, 1N1P, 1N4U, 1N4V, 1N4W, 2GEW, and 3COX.