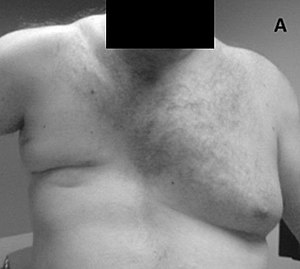
Poland anomaly

Poland syndrome is a birth defect characterized by an underdeveloped chest muscle and short webbed fingers on one side of the body. Short ribs, less fat, and breast and nipple abnormalities may also occur on that side. Typically the right side is involved. People generally have normal movement and health. Poland syndrome is a birth defect characterized by an underdeveloped chest muscle and short webbed fingers on one side of the body. Short ribs, less fat, and breast and nipple abnormalities may also occur on that side. Typically the right side is involved. People generally have normal movement and health. The cause is unknown. One theory is that it is due to disruption of blood flow during development before birth. The condition is generally not inherited from a person's parents. No genes that contribute to the disorder have been identified. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. Often people remain undiagnosed and some may not realize they are affected until puberty. Treatment depends on the severity and may include surgical correction. About 1 in 20,000 newborns are affected. Males are affected twice as often as females. It is named after Alfred Poland who described the condition when he was a student in 1841. A list of the common side effects broken down by frequency. Very frequent Frequent Occasional It is usually considered a unilateral condition. Some have claimed that the term can be applied in bilateral presentation, but others recommend using alternate terminology in those cases. The cause of Poland syndrome is unknown. However, an interruption of the embryonic blood supply to the arteries that lie under the collarbone (subclavian arteries) at about the 46th day of embryonic development is the prevailing theory.