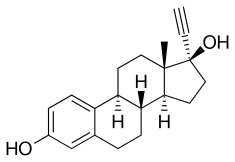
Ethinylestradiol

Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. It is also occasionally used as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used alone for various indications such as the treatment of gynecological disorders and prostate cancer. It is usually taken by mouth. Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. It is also occasionally used as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used alone for various indications such as the treatment of gynecological disorders and prostate cancer. It is usually taken by mouth. The general side effects of EE include breast tenderness and enlargement, headache, fluid retention, and nausea among others. In men, EE can additionally cause breast development, feminization in general, hypogonadism, and sexual dysfunction. Rare but serious side effects include blood clots, liver damage, and cancer of the uterus. EE is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol. It is a synthetic derivative of estradiol, a natural estrogen, and differs from it in various ways. Compared to estradiol, EE has greatly improved bioavailability when taken by mouth, is more resistant to metabolism, and shows relatively increased effects in certain parts of the body like the liver and uterus. These differences make EE more favorable for use in birth control pills than estradiol, though also result in an increased risk of blood clots and certain other rare adverse effects. EE was developed in the 1930s and was introduced for medical use in 1943. The medication started being used in birth control pills in the 1960s. Today, EE is found in almost all combined forms of birth control pills and is nearly the exclusive estrogen used for this purpose, making it one of if not the most widely used estrogens. There are many uses for EE. It is most commonly used as contraception in combined oral contraceptives (COC), also known as birth control, to prevent pregnancy after sex. EE in its birth control formulation is not only used to prevent pregnancy, but can also be used to treat absence of menstruation, symptoms during menstruation, and acne. EE is also used as menopausal hormone therapy. The main reason for using HRT in menopausal women is to relieve common vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and flushing. Studies have found that estrogen replacement helps improve these symptoms when compared to a placebo. Other common menopause symptoms such as vaginal dryness (which can cause pain during sexual intercourse), vaginal itching, and depressed mood, can benefit from HRT. In addition to treatment of menopausal symptoms, EE has been used as a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. However, it is no longer commonly used nor recommended for this purpose, with estradiol having largely superseded it. EE can also be used to treat hypogonadism in women, prevent osteoporosis in women, and has been used as palliative care for prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women. EE or any estrogen alone is contraindicated for women who have a uterus due to the increased risk of endometrial cancer; giving a progestogen with an estrogen mitigates the risk.