APLP2

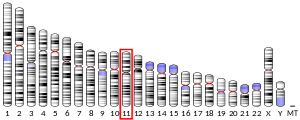
33411804ENSG00000084234ENSMUSG00000031996Q06481Q06335NM_001328682NM_001328684NM_001328685NM_001328686NM_001102455NM_001102456NM_009691NM_001357698NP_001315613NP_001315614NP_001315615NP_001633NP_001095925NP_001095926NP_033821NP_001344627Amyloid-like protein 2, also known as APLP2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APLP2 gene. APLP2 along with APLP1 are important modulators of glucose and insulin homeostasis. Amyloid-like protein 2, also known as APLP2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APLP2 gene. APLP2 along with APLP1 are important modulators of glucose and insulin homeostasis. The human APLP2 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 11 at region 2 band 4, from base pair 130, 069, 821 to base pair 130, 144, 811 (GRCh38.p7). APLP2 consists of 763 amino acids, with 31 amino acids making up the signal peptide and 732 amino acids making up the chain of the protein. The extracellular domain (residues 32-692) contains the E1 domain, E2 domain, and BPTI/Kunitz inhibitor domain. The E1 domain contains two independent folding units, the growth factor-like domain (GFLD) and the copper-binding domain (CuBD). GFLD has a highly charged basic surface and a highly flexible region consisting of an N-terminal loop formed by a disulphide bridge. CuBD consists of an alpha-helix that is tightly packed on a triple-stranded beta-sheet. The E2 domain is the largest subdomain of APLP2 and consists of six alpha-helixes. The N-terminal double stranded coiled coil structure of the first monomer of E2 packs against the C-terminal triple stranded coiled coil structure of the second monomer. The BPTI/Kunitz inhibitor domain (residues 306-364) is ‘Cys-rich’ and is capable of inhibiting several proteases. The ectodomain of APLP2 is dimeric and contains multiple binding sites for metal ions and components of the extracellular matrix. These bindings site can bind copper, zinc, collagen and heparan sulfate. The transmembrane region of APLP2 (residues 693-716) is helical in structure. The cytoplasmic domain (resides 717-763) contains a YENPTY sequence suggesting a duel function of the domain. The NPxY motif can function as a signal for endocytosis or the sequence can function to mediate binding of various interactive partners.