Hepatoportoenterostomy

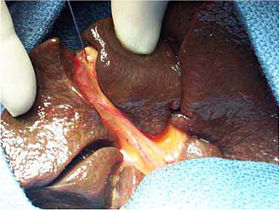
A hepatoportoenterostomy or Kasai portoenterostomy is a surgical treatment performed on infants with Type IVb choledochal cyst and biliary atresia to allow for bile drainage. In these infants, the bile is not able to drain normally from the small bile ducts within the liver into the larger bile ducts that connect to the gall bladder and small intestine. A hepatoportoenterostomy or Kasai portoenterostomy is a surgical treatment performed on infants with Type IVb choledochal cyst and biliary atresia to allow for bile drainage. In these infants, the bile is not able to drain normally from the small bile ducts within the liver into the larger bile ducts that connect to the gall bladder and small intestine. The surgery involves exposing the porta hepatis (the area of the liver from which bile should drain) by radical excision of all bile duct tissue up to the liver capsule and attaching a Roux-en-Y loop of jejunum to the exposed liver capsule above the bifurcation of the portal vein creating a portoenterostomy. The rationale for this approach is that minute residual bile duct remnants may be present in the fibrous tissue of the porta hepatis and thus provide direct connection with the intrahepatic ductule system to allow bile drainage. This procedure was developed in 1951 by Japanese biliary and hepatic pediatric surgeon Morio Kasai (1922–2008). Prognosis of this condition/procedure comprises the following: