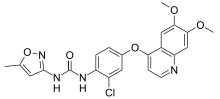
Tivozanib

Tivozanib (trade name Fotivda) is an oral VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It has completed a Phase 3 investigation for the treatment of first line (treatment naive) patients with renal cell carcinoma. The results from this first line study did not lead to US FDA approval, but tivozanib was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in August 2017.RET inhibitors: Vandetanib (also VEGFR and EGFR). Entrectinib (ALK, ROS1, NTRK).c-MET inhibitor: Cabozantinib (also VEGFR2). Tivozanib (trade name Fotivda) is an oral VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It has completed a Phase 3 investigation for the treatment of first line (treatment naive) patients with renal cell carcinoma. The results from this first line study did not lead to US FDA approval, but tivozanib was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in August 2017. Tivozanib must not be combined with St. John's Wort, an inducer of the liver enzyme CYP3A4 (see interactions below). It should not be taken during pregnancy as it is teratogenic, embryotoxic and fetotoxic in rats. The most common side effects in studies were hypertension (high blood pressure, in 48% of patients), dysphonia (hoarse voice, 27%), fatigue and diarrhoea (both 26%). A hypertensive crisis occurred in 1% of patients. Administration of a single dose of tivozanib with rifampicin, a strong inducer of the enzyme CYP3A4, cuts the biological half-life and total exposure (AUC) of tivozanib in half, but has no relevant influence on highest concentrations in the blood. Combination with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, has no relevant effects. The clinical significance of these findings is not known. A quinoline urea derivative, tivozanib suppresses angiogenesis by being selectively inhibitory against vascular endothelial growth factor. It was developed by AVEO Pharmaceuticals. It is designed to inhibit all three VEGF receptors. After tivozanib is taken by mouth, highest blood serum levels are reached after 2 to 24 hours. The total AUC is independent of food intake. When in the bloodstream, over 99% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins, predominantly albumin. Although the enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP1A1 and several UGTs are capable of metabolising the drug, over 90% circulate in unchanged form. The metabolites are demethylation, hydroxylation and N-oxidation products and glucuronides. The biological half-life is 4.5 to 5.1 days; 79% being excreted via the faeces, mostly unchanged, and 12% via the urine, completely unchanged. Tivozanib is used in form of the hydrochloride monohydrate, which is a white to light brown powder. It is practically insoluble in water and has low solubility in aqueous acids, ethanol and methanol. It is not hygroscopic and not optically active. Phase III results on advanced renal cell carcinoma suggested a 30% or 3 months improvement in median progression-free survival compared to sorafenib but showed an inferior overall survival rate of the experimental arm versus the control arm. The Food and Drug Administration's Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee voted in May 2013 13 to 1 against recommending approval of tivozanib for renal cell carcinoma. The committee felt the drug failed to show a favorable risk-benefit ratio and questioned the equipose of the trial design, which allowed control arm patients who used sorafenib to transition to tivozanib following progression disease but not those on the experimental arm using tivozanib to transition to sorafenib. The application was formally rejected by the FDA in June 2013, saying that approval would require additional clinical studies.